Environmental goods and services sector (EGSS)
Due to the global challenges in the fields of climate protection, environmental protection and resource conservation, the environmental economy is becoming increasingly important. The environmental economy produces goods and services such as products from organic farming, renewable energy, low-energy and passive houses or the treatment of waste and wastewater that serve one of two purposes: protecting the environment or preserving natural resources.

In 2019, the European Commission adopted the Green Deal - an ambitious roadmap for a sustainable, resource-efficient and competitive economy. The goods and services produced by the environmental economy are central to this goal. The accounts on the environmental goods and services sector (EGSS) enable analyses of environmental employment as well as developments in green production, gross value added and exports and will also serve to evaluate the objectives of the European Green Deal. The gross value added of environmental goods and services sector represents the contribution of the environmental economy to GDP.
The transition to a circular, less resource-intensive economy is a key objective of the European Green Deal. In addition to classic environmental protection, resource management is becoming increasingly important. A structural change from end-of-pipe to integrated technologies has been observable already for years. Environmental technologies and products conserve natural resources and contribute to their most efficient use.
In order to take into account the growing need for information on the environmental economy, the concept of environmental goods and services sector was developed over twenty years ago. The accounts on the environmental goods and services sector are part of the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting 2012 - Central Framework (SEEA-CF), which serves as an international standard. In the European context, the first pilot data collections were started in 2009. In Austria, key figures about the environmental economy have been compiled annually since 2008.
Regulation (EU) 538/2014 included the Environmental goods and services accounts in the regulation on European environmental economic accounts (VO (EU) 691/2011), putting the calculation on a legal basis. With the aim of making environmental economics as comparable as possible at European level, this Regulation has been supplemented by Implementing Regulation (EU) 2174/2015, which, amongst others, also lists the environmental goods and services that are to be included in the EGSS. The Handbook on Environmental goods and services accounts published by Eurostat provides comprehensive instructions and recommendations on data compilation. In 2017, the final values for 2014 and 2015 were submitted to Eurostat for the first time.
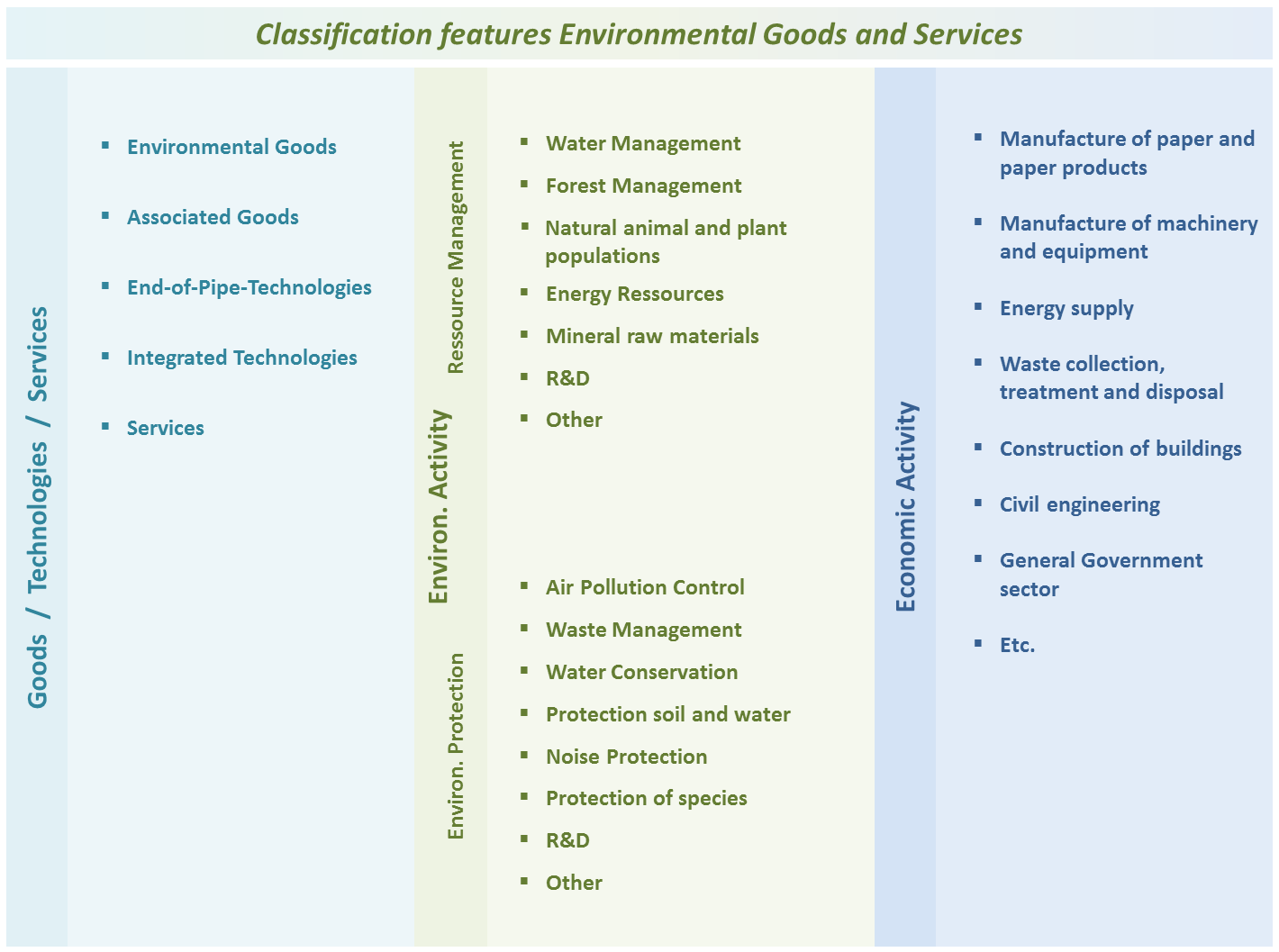
The production value, gross value added, exports and the associated employment achieved with environmental economy are presented broken down by several classifications:
- Type of economic output: market activities, non-market activities, ancillary activities, activities for own final use
- Type of environmental product: Environmental services, Connected goods, Adapted goods, End-of-pipe technologies, Integrated technologies
- Environmental protection and resource management activities: Classification systems CEPA for environmental protection activities and CReMA for resource management activities
- Economic sectors: ÖNACE at 2-digit level
- Regional structure: federal states